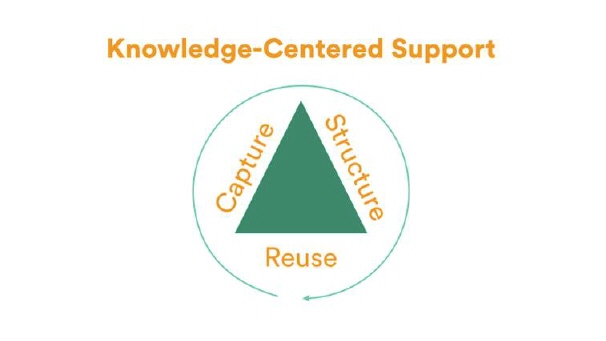
Knowledge Centered Support is a methodology that focuses on knowledge as a key asset of the organization. KCS is not something to do in addition to solving issues, KCS becomes the way in which you resolve issues. KCS does not replace the knowledge and experience of your support agents—rather, it complements them. Organizations that have implemented KCS report dramatic improvements in operating costs, incident/request resolution, customer satisfaction, job satisfaction, and significant reduction in training times.

Knowledge-centered support
Use case example
Knowledge-centered support follows a continuous loop of capturing, structuring, and reusing content.
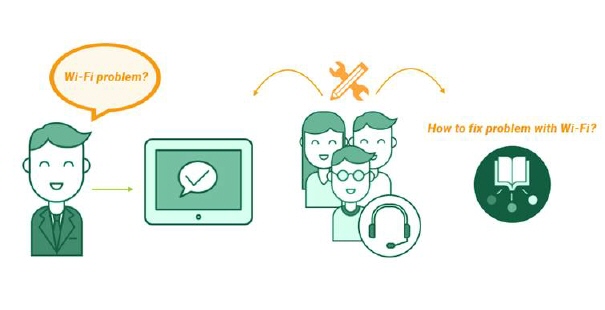
Step 1: Capture Knowledge
Knowledge starts with the customer. When requests come in, articles are created as a by-product of the problem-solving process. This means that your team writes articles in the customer context, making information inherently relevant and easily searchable.
Our system offer possibility of creating articles from ticket comments. You can find detailed description of this feature here: Creating article from ticket comment, or agent can manually write article from customer requests. Functionality for Adding new article is described in detail here.
Capture knowledge
Step 2: Structure Knowledge
The best way to write an article from the customer’s perspective is to work from a template or form. This keeps things simple for service desk agents and promotes consistency in the knowledge base.
Our knowledge base have default KB categories and KB article types. Here is also a possibility for creating custom categories and article types as well as creating custom templates for article types. You can find detailed description of these features here: Knowledge Base Categories and Knowledge Base Article Types.
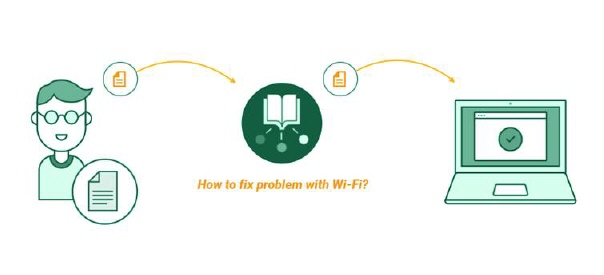
Step 3: Reuse Knowledge
When working on customer issues, agents should search through the knowledge base. They can then link requests to relevant articles, making sure the team works from their collective knowledge.
KB Article can be associated with the configuration items, other articles or the ticket and vice versa.
Reuse Knowledge
Step 4: Improve Knowledge
The next step is improving content. When agents reuse articles in their problem-solving process, they’re reviewing them at the same time. Frequently used articles are constantly being seen and therefore remain current. This keeps your knowledge up-to-date and shares ownership across the entire team. Once an article is ready, it can be published.
Improve knowledge
Step 5: Content Health
One way of improving the quality of your content is knowledge monitoring. Measure how effective each article is at solving problems and only put resources toward high-demand, cost-reducing knowledge.
For article content health our system use feedbacks. Article feedback is the way the user can give his opinion of the quality and usefulness of the KB Article. User can rate KB Article with star (five star points rating system is in use) or flag article with like/dislike to set if they find the KB Article helpful or not.
There’s more to knowledge-centered support than just process. Cultural changes play a big part—applying KCS shifts your team from relying on individual experiences to working from collaborative knowledge. Collective wisdom enables more than just the service desk team, it provides resources for organizational learning and helps onboard new agents as they come.